History Array
H: numpy structured array
A record of runtime attributes and output data for all ensemble members.
Overview
libEnsemble uses a NumPy structured array to store information about each point (ensemble member) generated and processed in the ensemble.
The manager maintains a global copy. Each row contains:
Data generated by the gen_f
Resultant output from the sim_f
Reserved fields containing metadata
When the history array is initialized, it creates fields for each
gen_specs["out"] and sim_specs["out"] entry. These entries may resemble:
gen_specs["out"] = [("x", float, 2), ("theta", int)]
sim_specs["out"] = [("f", float)]
Therefore, the gen_f and sim_f must return output as NumPy
structured arrays for slotting into these fields.
Ensure input/output field names for a function match each other or a reserved field:
gen_specs["out"] = [("x", float, 2), ("theta", int)] # produces "x" and "theta"
sim_specs["in"] = ["x", "theta", "sim_id"] # accepts "x", "theta" and "sim_id", a reserved field
Reserved Fields
User fields and reserved fields are combined together in the final History array returned by libEnsemble.
These reserved fields can be modified to adjust how/when a point is evaluated:
sim_id[int]: Each unit of work must have asim_id. This can be set by the generator or by the manager by default. Users should ensure these IDs are sequential and unique when running multiple generators.
cancel_requested[bool]: Can be setTruein a generator to request attempted cancellation of the corresponding simulation.
The following fields are automatically populated by libEnsemble:
gen_worker [int]: Worker that generated this entry
gen_started_time [float]: Time gen_worker was initiated that produced this entry
gen_ended_time [float]: Time gen_worker requested this entry
sim_worker [int]: Worker that did (or is doing) the sim evaluation for this entry
sim_started [bool]: True if entry was given to sim_worker for sim evaluation
sim_started_time [float]: Time entry was given to sim_worker for a sim evaluation
sim_ended [bool]: True if entry’s sim evaluation completed
sim_ended_time [float]: Time entry’s sim evaluation completed
gen_informed [bool]: True if gen_worker was informed about the sim evaluation of this entry
gen_informed_time [float]: Time gen_worker was informed about the sim evaluation of this entry
kill_sent [bool]: True if a kill signal was sent to worker for this entry
Other than "sim_id" and cancel_requested, these fields cannot be
overwritten by user functions unless libE_specs["safe_mode"] is set to False.
Warning
Adjusting values in protected fields may crash libEnsemble.
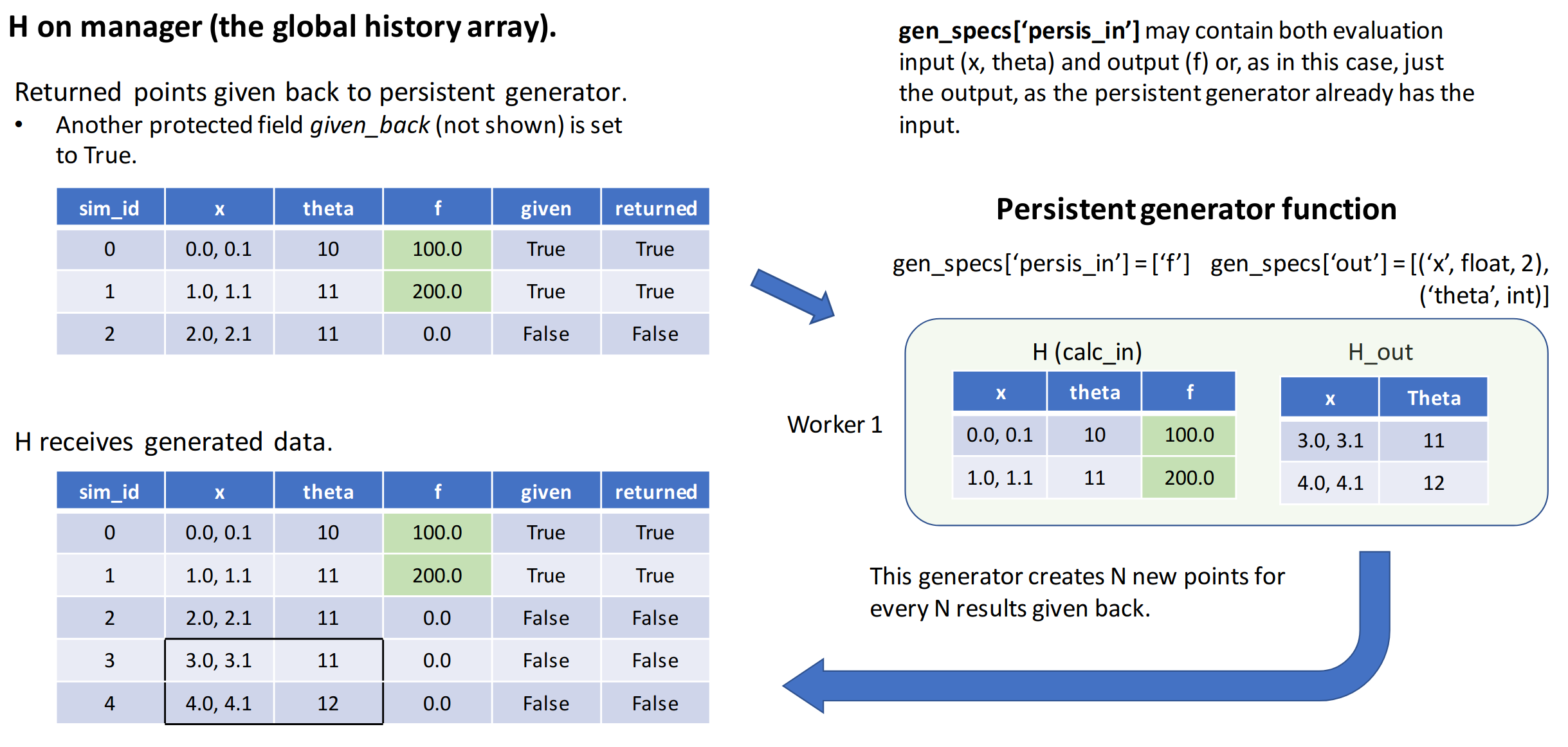
Example Workflow updating History
Step 1: The history array is initialized on the manager
The history array is initialized using the libEnsemble reserved field and the
user-provided gen_specs["out"] and sim_specs["out"] entries.
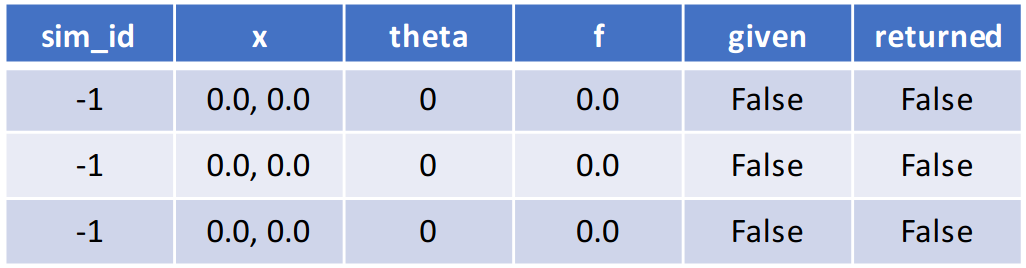
In the figure below, only the
reserved fields: sim_id, sim_started, and sim_ended are shown for brevity.
gen_f and sim_f functions accept a local history
array as the first argument that contains only the rows and fields specified.
For new function calls these will be specified by either gen_specs["in"] or
sim_specs["in"]. For generators this may be empty.
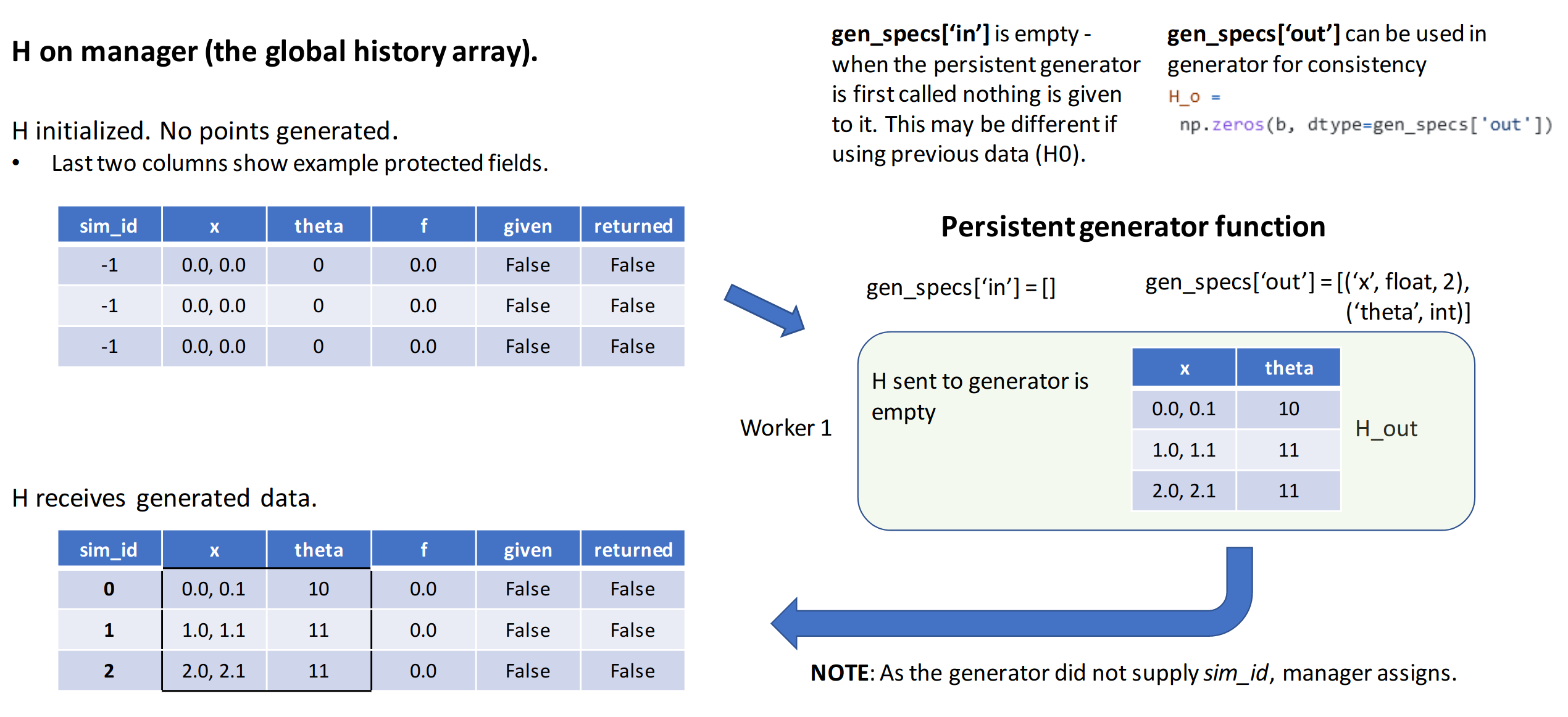
Step 2: Persistent generator gen_f is called
Step 3: Points are given out for sim_f to evaluate
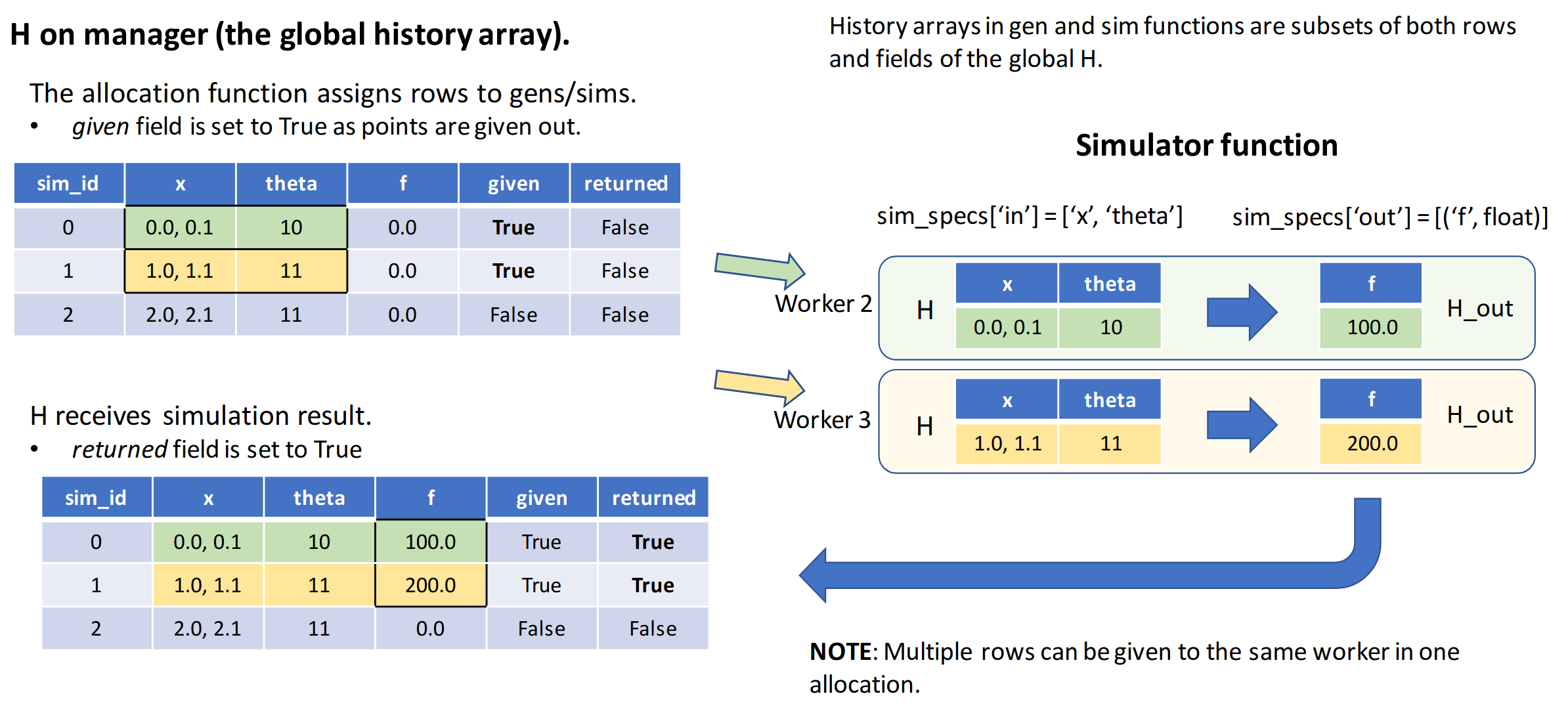
Step 4: Results returned to persistent generator gen_f